Extrinsic eye muscles F. They lie pri-marily in the dermis and project onto the surface through the epidermis.

Accessory Structures Of The Skin Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
They can extend down through the dermis into the hypodermis.

. Accessory structures of the skin include all of the following except Hypodermis. Accessory structures of the skin include hair nails sweat glands and sebaceous glands. Accessory structures of the skin include all of the following except A hair follicles.
These structures embryologically originate from the epidermis and can extend down through the dermis into the hypodermis. Study the definition of skin accessory structures the functions and structure of the hair and hair loss. Accessory structures of the skin include all of the following except A hair follicles.
Modulating body temperature and electrolyte balance. These structures embryologically originate from the epidermis and can extend down through the dermis into the hypodermis. Accessory structures of the skin include all of the following except A hair follicles.
The hair is a keratin structure growing out of the epidermis. The skin and accessory structures are the largest organ system in the human body. Hair Hair is a keratinous filament growing out of the epidermis.
Accessory structures of the skin include hair nails sweat glands and sebaceous glands. The type of cells that form the strata in the epidermis are A adipocytes. Hair is composed of the following structures.
Accessory structures of the skin include all of the following except. Learning Objective Classify eccrine and apocrine sweat glands Key Takeaways Key Points Sweat glands are located deep within the skin and primarily regulate temperature. And synthesizing vitamin D.
It is primarily made of dead keratinized cells. The integumentary system is the scientific name for the skin and its accessory structures. It is primarily made of dead keratinized cells.
A Accessory structures of the skin include all of the following except A. Scar tissue is the result of A thickened corneum in the area of the injury. Accessory structures of the skin include hair nails sweat glands and sebaceous glands.
E dendriticȱcells B keratinocytes. The accessory structures protect lubricate and move the eye. All of the following are functions of accessory structures of integument except A.
These structures embryologically originate from the epidermis and can extend down through the dermis into the hypodermis. In fact the skin and accessory structures are the largest organ system in the. Production of skin pigments.
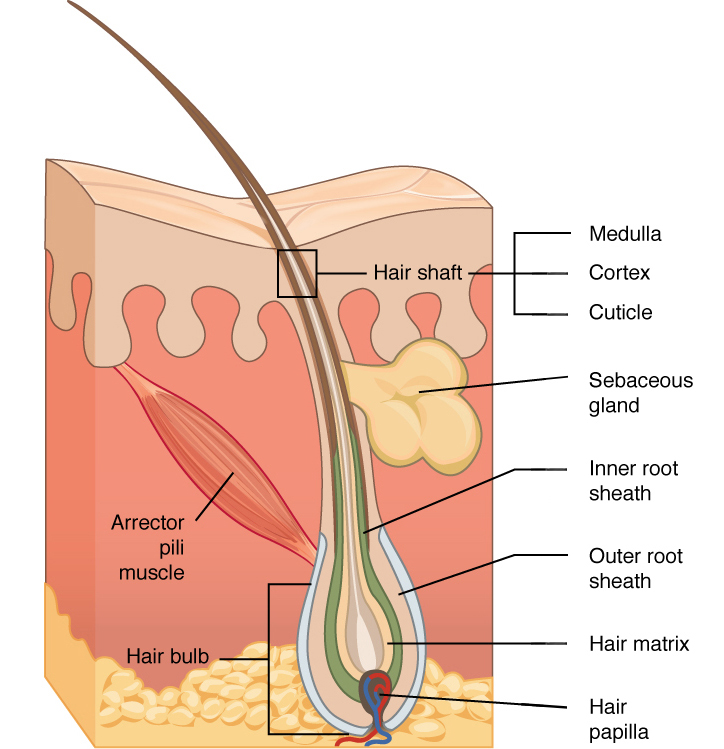
The hair shaft is the portion of the hair that is visible on the surface of the skin. Hair Hair is a keratinous filament growing out of the epidermis. The following accessory organs skin derivatives are embedded in the skin.
The sclera is the firm white outer connective tissue layer of the posterior five-sixths of the fibrous tunic. A thickened stratum germinativum Basale in the area of the injury. They include all of the following EXCEPT.
These structures embryologically originate from the epidermis and can extend down through the dermis into the hypodermis. Hairs are elongated filaments of keratinized epithelial cells that arise and emerge from the skin of mammals. Hair Hair is a keratinous filament growing out of the epidermis.
An abnormally large number of collagen fibers. The skin and accessory structures perform a variety of essential functions such as protecting the body from invasion by microorganisms chemicals and other environmental factors. Accessory structures of the skin include hair nails sweat glands and sebaceous glands.
These structures embryologically originate from the epidermis and can extend down through the dermis into the hypodermis. E nails D epidermis. The results of both fibrosis and regeneration are exactly the same.
HAIR Hair is a keratinous filament growing out of the epidermis. These structures embryologically originate from the epidermis and are often termed appendages. In the adult human body the skin makes up about 16 percent of body weight and covers an area of 15 to 2 m 2.
52 ACCESSORY STRUCTURES OF THE SKIN Accessory structures of the skin include hair nails sweat glands and sebaceous glands. Accessory structures of the skin include hair nails sweat glands and sebaceous glands. Generally skin especially on the face and hands starts to display the first noticeable signs of aging as it loses its elasticity over time.
Accessory Structures of the Skin Sweat Sudoriferous Glands Sweat glands also known as sudoriferous glands are distributed over most of the body surface. Accessory structures of the skin include the hair nails sweat glands and sebaceous glands. It is primarily made of dead keratinized cells.
Hair Hair is a keratinous filament growing out of the epidermis. It is primarily made of dead keratinized cells. These structures embryologically originate from the epidermis and can extend down through the dermis into the hypodermis.
The integumentary system refers to the skin and its accessory structures. These structures embryologically originate from the epidermis and can extend down through the dermis into the hypodermis. During the process of inflammation injury stimulates mast cells to release A.
Janet Ramsden The accessory structures also have lowered activity generating thinner hair and nails and reduced amounts of sebum and sweat. Hair follicles originate in the. It is primarily made of dead keratinized cells.
ACCESSORY STRUCTURES The accessory structures of the skin include the sweat glands sebaceous glands hair and nails. Hair Hair is a keratinous filament growing out of the epidermis. Acting as a sensory organ.
Figure 533 Aging. Accessory structures of the skin include hair nails sweat glands and sebaceous glands. O O Sebaceous glands.
Accessory organs of the skin include.
Accessory Structures Of The Skin Biology For Majors Ii

Skin 2 Accessory Structures Of The Skin And Their Functions Nursing Times

Skin 2 Accessory Structures Of The Skin And Their Functions Nursing Times


0 Comments